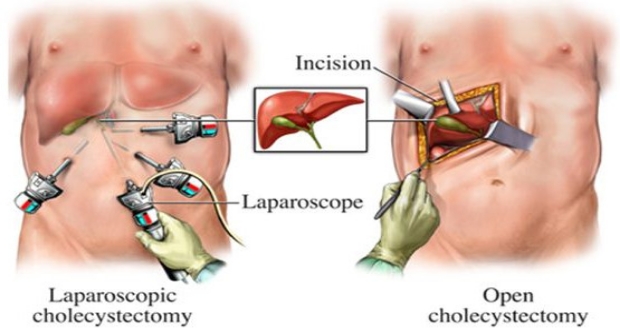
Surgical removal of gallbladder, known as cholecystectomy, is the usual treatment for symptomatic or complicated gallstones. There are two types of surgeries to remove gallbladder- open (traditional method) and laparoscopic (minimal invasive) method.
Gallbladder is a small organ present below the liver in upper right side of abdomen. It stores a green-yellow colored liquid known as bile that in turn helps with digestion. In most of the cases, gallstones are formed when there is too much cholesterol in bile.
Occasionally gall bladder stone may slip into the common bile duct, CBD, resulting in jaundice.
You may experience pain in the upper right abdomen. The gallbladder pain usually doesn’t last more than a few hours. Apart from pain, you may also experience the following signs.
Surgical removal of gallbladder-
During traditional surgery, 5-8 inch long incision is made in the abdomen just below your ribs on right side that goes to below your waist. Gallbladder is removed through this incision. This is called an open cholecystectomy.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the newer way to remove the gallbladder. This surgery is done using a laparoscope. Laparoscope is a small, thin tube that has a camera on tip which is used to see the inside of your body, giving a magnified view. Instead of one long incision, tiny cuts (usually ½ to 1 cm) are used to remove the gallbladder.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy involves the following steps-
Benefits of laparoscopic cholecystectomy-
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy has several advantages –
The surgery is done using needle instruments, as active forceps, in place of the 5 mm instruments used in laparoscopic surgery, thus further minimising the cuts.
Instead of making traditional four to five small incisions, a single small cut is made during SILS through which the surgeon then carries out surgery identical to a traditional laparoscopic one
Laparoscopic removal of CBD (common bile duct) stone-
Occasionally gall bladder stone may slip into the common bile duct, CBD, resulting in jaundice. CBD stone is then removed by endoscopy or laparoscopy and then gall bladder removal is done.
Intra Operative Cholangiography
In case of difficult cases, Selective dynamic Intra Operative Cholangiography using C-arm image intensifier is done for detection of Bile duct stones and confirmation of CBD anatomy.
Minimal Invasive Surgery – Minimised
Surgery has progressed from huge incisions in open surgery to multiple tiny incisions in laparoscopy and now to a single small cut in Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery (SILS) or scarless surgery.
SILS – Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery is an advanced modification of laparoscopic surgery. Instead of making traditional four to five small incisions, a single small cut is made during SILS through which the surgeon then carries out surgery identical to a traditional laparoscopic one. The laparoscope and all other surgical instruments are inserted through this single incision. In conventional laparoscopic surgery, usually, several small incisions of 0.5 to 1 cm are made while in Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery, only single incision of about 1.5 to 2 cm is made.
In SILS, the incision is typically placed at the patient’s umbilicus and so the scar is hidden and is closed with absorbable subcuticular sutures. This surgery is often known as “SCARLESS” surgery, as when the wound heals, it is almost invisible because it is hidden within the belly button. The healed incision leaves practically no scar, thus making SILS cosmetically a superior option.
Operations which can be performed with SILS
Currently, the following operations can be performed by SILS
Laparoscopic surgery has generally replaced the need for traditional open surgeries in the abdominal or pelvic cavities. SILS is the most recent technology. Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery has several advantages –
Hernia is protrusion of contents of abdomen like usually intestine or fat through an area of weakness in the abdominal wall.
It may occur through weak natural openings like-
Hernia may be precipitated due to too much strain on the abdominal wall such as persistent coughing, strain from heavy lifting, difficulty with urination or bowel movements, and obesity to a great extent. Due to weak inside layers of the abdominal wall, the inner lining of abdomen pushes through it and forms a balloon-like sac. This may result in serious health problems and complications. It can occur in men and women of all ages.
Types / sites of hernias –
How is a laparoscopic hernia repair done?
Laparoscopic surgery uses a thin, telescope-like instrument known as a laparoscope. A small incision is made usually at belly button through which this instrument is inserted. It is generally performed under general anaesthesia and thus you would be sleeping through the surgery.
The laparoscope has a tiny video camera on its tip that projects an inside view of your body onto a screen in the operating room. In order to cover the defects in the abdominal wall and strengthen the tissue, a mesh is placed on the inside.
