Posted by imhtechp no comments
When You and Your Baby Need Special Care
Your blood tests show that you have Gestational Diabetes. This doesn’t mean that you did anything wrong. And it doesn’t mean that your baby will be born with diabetes. But it does mean that you need to take special care of yourself, so you and your baby stay healthy.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is a special kind of diabetes that happens only during pregnancy (gestation). Changes that occur in your body while you’re pregnant cause your blood sugar to be too high. Gestational diabetes is more likely in women who:
Help from Your Healthcare Team
To have a healthy baby, you need to take special care of yourself. Your healthcare team will help you learn what to do.
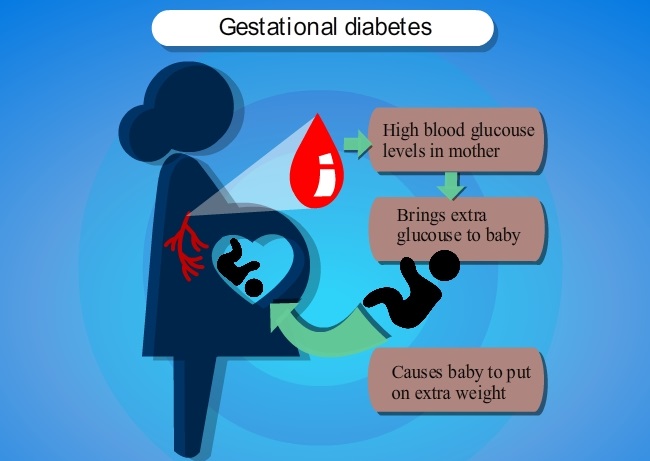
Understanding Blood Sugar Your body turns food into blood sugar to use for energy. Your blood sugar also goes to your baby. If your blood sugar level gets too high, it can cause problems for the baby and for you. You can help prevent these problems by controlling your blood sugar.
Too Much Blood Sugar Affects You and Your Baby If your body can’t use insulin properly, your blood sugar level gets too high. Then too much blood sugar goes to your baby. This can cause problems for both you and your baby.
Risks to You
If you don’t control your blood sugar, you are more likely to have these problems:
Risks to Your Baby
If you don’t control your blood sugar, your baby is more likely to have these problems:
Controlling Blood Sugar Helps Prevent Problems You can lower your blood sugar by eating right and exercising. You might also need to take insulin or oral medications. If you keep your blood sugar in control, the risks to you and your baby are the same as for a normal pregnancy.
How Much Weight Should You Gain?
You need to gain some weight so your baby will grow. But gaining too much weight can make your blood sugar harder to control.
Your weight was normal before pregnancy Gain 25 to 35 lbs.
You were overweight before pregnancy Gain 15 to 25 lbs.
You were underweight before pregnancy or are under 18 years old Gain 28 to 40 lbs.
You are having twins Gain 35 to 45 lbs.
Your total weight gain should be (ask your Gynecologist)
For You and Your Baby The health of you and your baby depends on how well you control your blood sugar. To do this, follow your meal plan every day. See your Doctor regularly. And, if you’re asked to do so, check your blood sugar at home. Doing all of these things helps make sure you and your baby stay healthy.
In case you have Gestational diabetes, feel free to send us a query or walk in for a consultation. Dr. Rimmi Singla(Senior Consultant Laparoscopic Gynaecologist & Obstetrician, IVF& Infertility Specialist) will always suggest you the best treatment depending on your diagnosis.
Leave a Reply
Be the First to Comment!